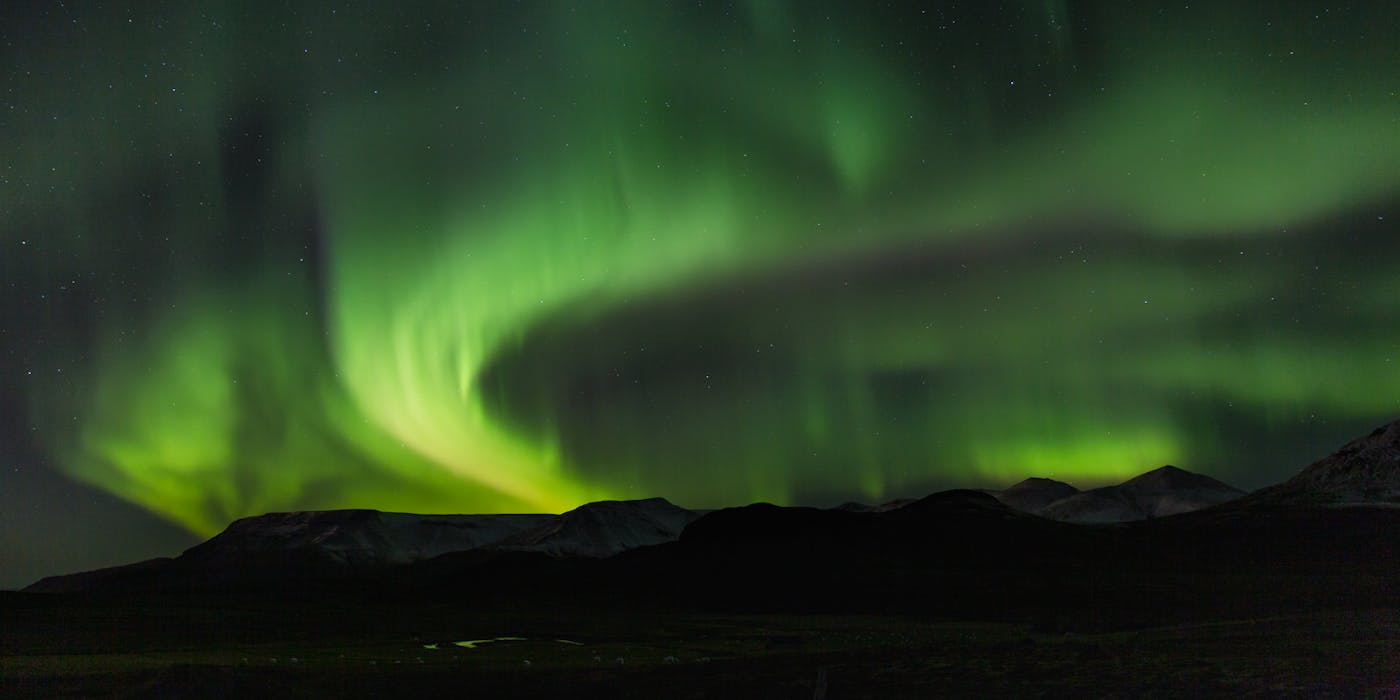
How to maximize your chances of seeing the Northern Lights
If you want the best chance of seeing the Northern Lights, the key is to be in the right place at the right time and know how to track them. Simply being within the Aurora Zone, the band across northern Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Canada, and Alaska will greatly increases your odds. But without the right tools or knowledge, your trip can be hit-or-miss, especially if you only have a few nights in the Arctic.
To really maximize your chances of witnessing this incredible natural light show, several factors need to line up:
- clear skies
- strong solar activity
- minimal light pollution
- and good timing.
By learning how to check aurora forecasts, monitoring space weather, and choosing the darkest possible locations, you’ll transform a random night of “aurora chasing” into a far better opportunity to see the Northern Lights in their full glory.
Important metrics for northern lights forecast
The Hello Aurora app is built on years of experience chasing the Northern Lights. We understand the frustration of missing this spectacular phenomenon and have designed the app to take that stress off your hands.
Let's look at the important metrics to check for Northern Lights hunting and why they are important.
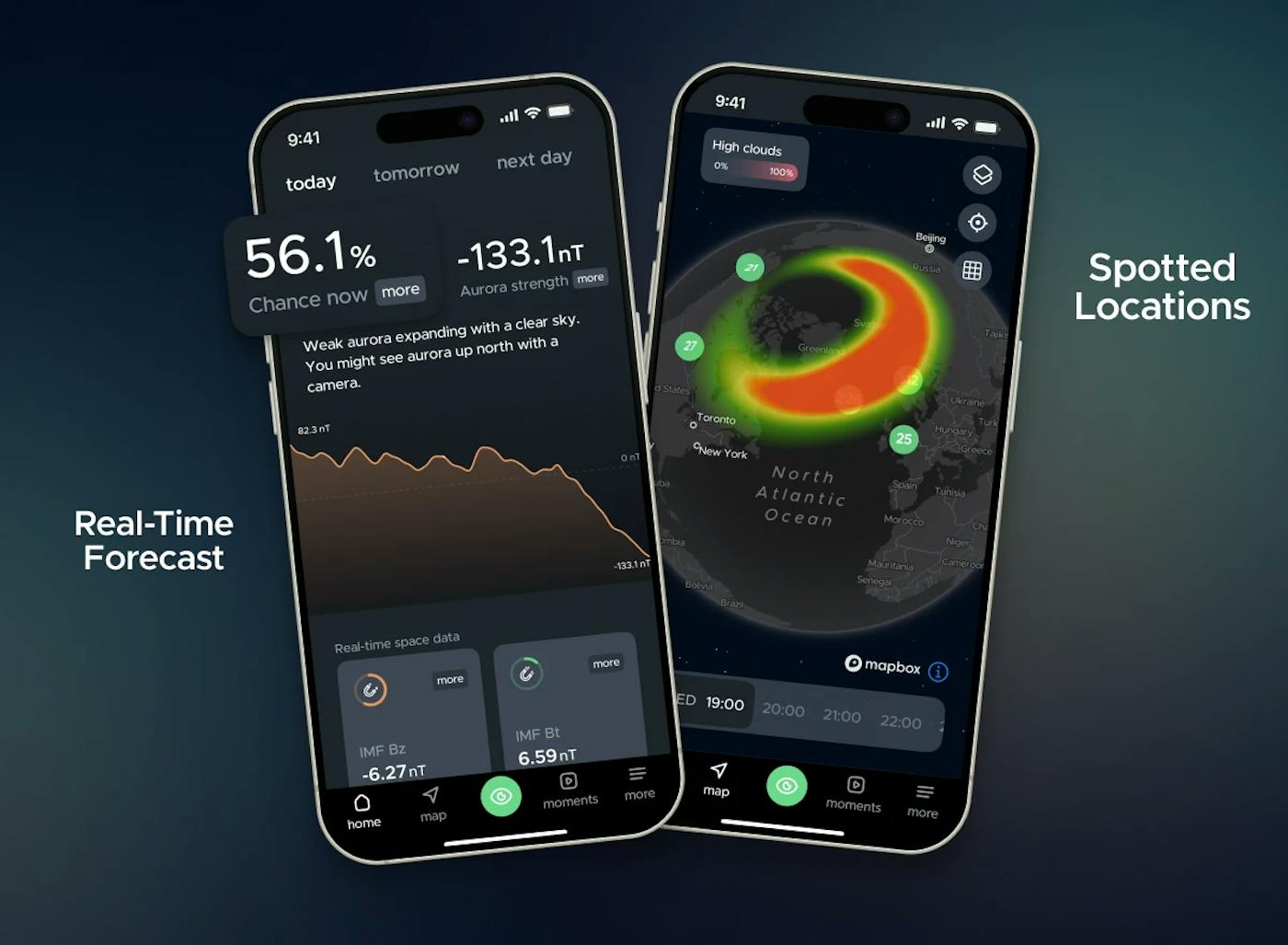
Aurora Strength
In 2020, Hello Aurora introduced Aurora Strength, a real-time Northern Lights forecasting metric based on magnetometer data from multiple space agencies monitoring the North Pole regions. A magnetometer measures fluctuations in Earth’s magnetic field caused by auroral activity.
Why Aurora Strength matters
Tracking Aurora Strength helps you predict when and where the Northern Lights will appear, for example:
- A sharp drop to ~-150 nT signals a substorm, meaning the aurora is likely to start dancing across the sky. The lower the value, the stronger the display, often linked to geomagnetic storms.
- A rise toward +150 nT shows the aurora is “charging,” often releasing a display within minutes.
- A return to ~5 nT means the aurora is temporarily quiet until the next shift.
Solar Wind
Just as you feel the wind more strongly when walking outside on a breezy day, the same principle applies to the solar wind.
- The faster the solar wind travels toward Earth, the more energy it transfers into the planet’s magnetic field.
- This increases the likelihood that the aurora will become brighter, more dynamic, and more visible in the night sky.
Monitoring solar wind speed is an important factor for predicting when and where the Northern Lights will put on their most spectacular displays.
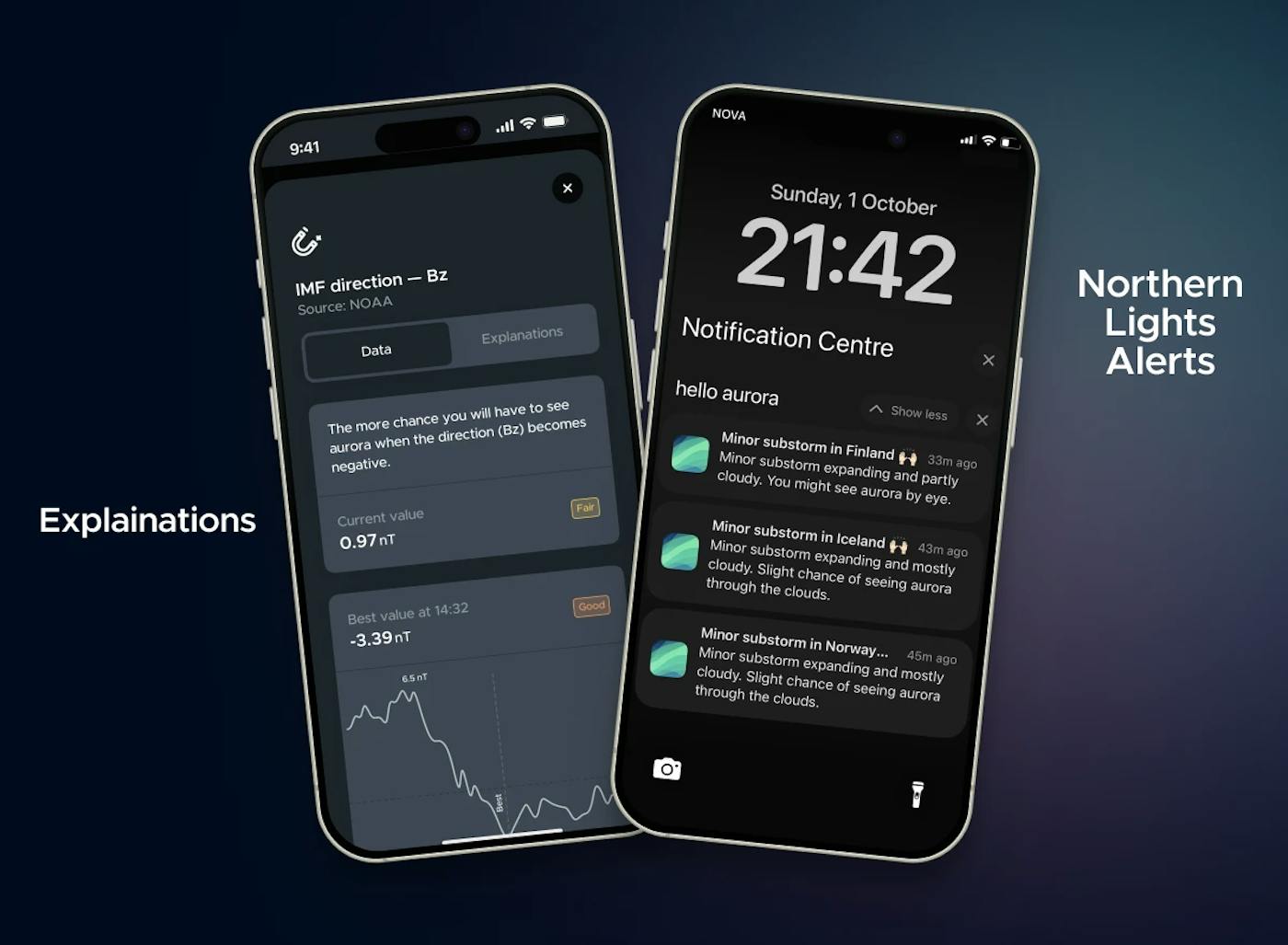
Interplanetary Magnetic Field
Planet Earth has two magnetic poles: north and south.
To understand how the aurora forms, think of two magnets: when opposite poles are brought close together, they naturally attract. A similar process occurs in space when the north-south orientation of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) points southward.
This orientation interacts with Earth’s magnetosphere, which is oriented northward. The resulting connection allows charged solar particles to penetrate the magnetosphere and collide with oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the upper atmosphere. These collisions release energy in the form of light, creating the spectacular displays we know as the aurora.